Schedule Ii Controlled Substance Laws
Texas Prescription Monitoring Program Frequently Asked Questions Regarding. A pharmacist may dispense a Schedule II controlled substances pursuant to a facsimile copy of an. Electronic copies of the drug laws and rules for the Prescription Monitoring Program are.
List of Controlled Substances (December 2018) This document is a general reference and not a comprehensive list. This list describes the basic or parent chemical and does not describe the salts, isomers and salts of isomers, esters, ethers and derivatives which may also be controlled substances. Scheduling Actions Controlled Substances List I and II Regulated Chemicals Exempted Lists Exempt Anabolic Steroid Products (February 6, 2015) Exempt Chemical Preparations (November 7, 2017) For Application Dates Through December 31, 2016 Exempted Prescription Products (October 24, 2018) Lists of Controlled Substances Disclaimer of the Controlled Substances Act ( et seq.) (CSA) lists substances which were controlled in 1970 when the CSA was enacted.
Since then many substances have been added, removed, or transferred from one schedule to another. The current list of controlled substances can be found in of the most recent issue of and the final rules which were published in the Federal Register subsequent to the issuance of the CFR. These lists describe the basic or parent chemical and do not describe the salts, isomers, salts of isomers, esters, ethers, and derivatives which may be controlled substances. These are not comprehensive lists so please note that a substance need not be listed as a controlled substance to be treated as a scheduled substance for criminal prosecution. The 'Other Names' column, provides some examples of alternate names for certain compounds, and in some instances provides examples of 'positional isomers'.
If outside parties want to ensure that a compound is not considered a scheduled substance or listed chemical, they should write the DEA, Drug and Chemical Evaluation Section (DRE), Diversion Control Division, 8701 Morrissette Drive, Springfield, Virginia 22152, for an official determination. A substance (not included on these lists) may also be regulated as a controlled substance analogue. A controlled substance analogue is a substance which is intended for human consumption, is structurally substantially similar to a schedule I or schedule II substance, is pharmacologically substantially similar to a schedule I or schedule II substance, or is represented as being similar to a schedule I or schedule II substance and is not an approved medication in the United States. See (32)(A) for the definition of a controlled substance analogue and for the schedule.
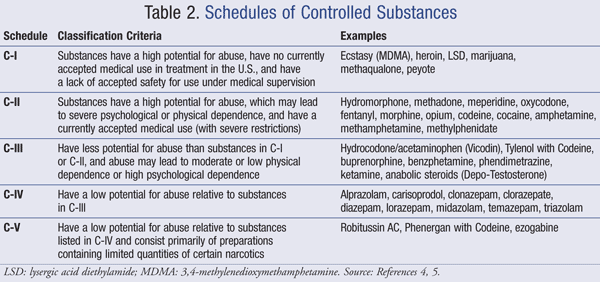
This second article of a 4-part series on key components of the Federal Controlled Substances Act will discuss the requirements for controlled substances prescriptions. For a prescription for a controlled substance to be considered valid, it must be “issued for a legitimate medical purpose by a registered practitioner acting in the usual course of sound professional practice.” Registered practitioner refers to any health care professional who is authorized to prescribe controlled substances within the area in which he or she is licensed to practice and who is registered with the Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) or is exempt from registration. All of the following must be included in a prescription for a controlled substance:. Manual signature of the prescriber Schedule II prescriptions must be presented to the pharmacy in written form and signed by the prescriber. There are no federal quantity limits on Schedule II prescriptions.
In addition, there is no federal time limit on when a Schedule II prescription must be filled after being signed by a prescriber. That being said, the pharmacist must ensure that the controlled substance is being prescribed for a legitimate medical purpose; the quantity of the medication prescribed and the time between signing and filling of a prescription may play a role in this decision. Note that state laws may have stricter rules. A prescription for a Schedule II medication may be phoned into the pharmacy in an emergency situation.
The prescriber must follow-up the phone prescription with a written prescription to the pharmacy within 7 days. Faxed Schedule II prescriptions are generally permitted, however, the pharmacist must receive the original, signed written prescription before dispensing the Schedule II controlled substance to the patient. There are 3 scenarios in which a facsimile Schedule II prescription may serve as an original written prescription. These include the following:. The provider is prescribing Schedule II medications to a patient in hospice care as certified by Medicare or licensed by the state. Prescriptions for Schedules III to V controlled substances may be written, orally communicated, or faxed to the pharmacy.
Not all prescriptions for controlled substances can be refilled. Schedule II medications may not be refilled; a new prescription must be written every time. Medications classified as Schedule III or IV controlled substances may be refilled up to 5 times in a 6-month period. Schedule V medications may be refilled as authorized by the prescriber.
For refills of any controlled substance, the dispensing pharmacist’s initials, date of refill, and amount dispensed must be written on the back of the prescription. One mechanism to verify the validity of a controlled substance prescription is through the DEA registration number provided by the practitioner. DEA registration numbers contain 2 letters followed by a computer-generated sequence of 7 numbers. The first letter in the DEA registration is generally an A, B, or M. Prior to October 1, 1985, DEA registration numbers began with the letter A. Registration numbers issued after this date start with the letter B. Mid-level practitioners, such as advanced nurse practitioners and physician assistants, have registration numbers beginning with the letter M.
The second letter in the registration number is the first letter of the practitioner’s last name (ie, J for Jackson or W for White). The computer-generated sequence of numbers can be verified using the following formula: add the sum of the first, third, and fifth digits to twice the sum of the second, fourth, and sixth digits. The total should be a number whose last digit is the same as the last digit of the DEA number on the prescription. Health care providers with prescribing authority, when acting within the usual course of business at a hospital or other health care institution, may prescribe controlled substances under the DEA registration number of the hospital or institution.
Examples of practitioners who may use a hospital’s DEA registration number include physician interns and residents as well as medical house staff or mid-level practitioners such as physician assistants or advanced nurse practitioners. The hospital or other institution must authorize the health care provider to prescribe under its registration number. A specific internal code number must be assigned to each authorized practitioner. The health care institution must keep an up-to-date list of all internal codes with the corresponding practitioner. If the pharmacy has any doubt regarding a controlled substance prescription from a provider using a health care institution’s DEA number, the pharmacist may contact the institution to verify the legitimacy of the prescription. As mentioned previously, mid-level practitioners such as nurse midwives, nurse practitioners, nurse anesthetists, clinical nurse specialists, physician assistants, and optometrists may be granted DEA registration numbers and may prescribe controlled substances. However, registration is contingent upon authority granted by the state in which they are licensed.
Schedule I Controlled Substance List
Pharmacists must be familiar with the controlled substances act in their state to determine which health care providers may or may not prescribe any controlled substances and, if so, which schedules may be prescribed. On December 19, 2007, a DEA regulation came into effect that allows a prescriber to issue multiple prescriptions authorizing an individual patient to receive a total of up to a 90-day supply of a Schedule II controlled substance. However, this is allowable only under the following conditions:.